Did you know that serving in a country’s army to protect the interests and lives of its people is the best honour one can experience as a professional? The armed forces of India hire capable and suitable candidates for various posts in the Indian army to safeguard a country from dangers and threats.
So, when it comes to appointing officers in the defense department, the main question is, what kind of officers does the President of India appoint? Well, in India, the President generally appoints two kinds of army officers. The first one is known as a Group A or Class 1 officer. This officer is known as a commissioned officer.
On the other hand, there are Group B or Class 2 officers who are known as non-commissioned officers. If you are looking to know more about the duties and ranks of a commissioned officer in the army, you are at the right place. In this blog, we will take a look at the ranks, types, and duties of a commissioned officer in Indian Army.
Types of Commissioned Officers in the Indian Military
Here are some of the types of a commissioned officer in the Indian military:
A. Indian Army
1. General Cadre Officers
The general cadre officers in the Indian Army are among the highest ranks, generally beginning from major general and progressing to the bigger and higher posts of General. What are their duties? Well, from strategic planning to the whole Command of large units, they play a vital role in shaping the tactics and operations of the army.
2. Technical Officers
Did you know that the lieutenant rank in Indian Army is one of the well-respected posts? It is as revered as the technical officers in the Indian Army, who manage and oversee the technical aspects of the army, such as electronics communication, engineering, and other technical fields. In case you didn’t know, a technical commissioned officer is involved in designing, planning, and managing technical projects.
B. Indian Navy
1. Executive Branch Officers
You already know that the NCO’s meaning and duties vary from those of a commissioned officer. But did you know that the executive branch officer’s responsibilities vary a lot from the NCO ranks?
Well, for starters, these officers are responsible for the administrative and operational management of aircraft, naval ships, submarines, and shore establishments. They play a crucial role in ensuring the readiness and effectiveness of the Indian Navy.
2. Technical Branch Officers
The technical branch officer is a commissioned officer rank in the Indian Navy where the responsibilities include repair, maintenance, and operation of the technical systems of the Navy. These officers are highly skilled and trained experts who play a vital role in maintaining the Navy’s technological superiority at sea.
C. Indian Air Force
1. Flying Branch Officers
Yes, the responsibilities of a flying branch officer are just as interesting as you have imagined. For starters, the duties of the commissioned officer here vary from the non-commissioned officer ranks. These experts are responsible for operating and plotting aircraft across different missions, including transport, combat, refuelling, and reconnaissance.
2. Ground Duty Branch Officers
These officers carry out a wide array of duties that are non-flying but vital for the effectiveness and functioning of the Air Force. These officers are held responsible for logistical, support, administrative, and technical functions, which are the key to maintaining operational readiness and efficiency.
Also Read:
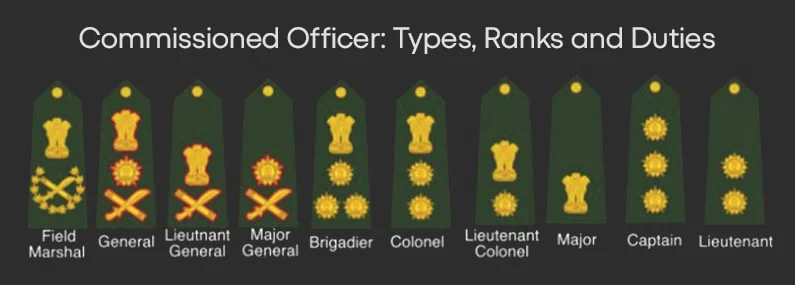
Commissioned Officer Ranks in the Indian Military
Let us now take a look at the different ranks of a commissioned officer:
A. Indian Army Ranks
1. Second Lieutenant
If we are to talk about the roles and responsibilities of a non-commissioned officer in Indian Army, you will notice how much it varies from the duties of a commissioned officer in the army.
Take the second lieutenant, for example; their duties are way more diverse than the NCO ranks.
2. Lieutenant
In the Indian armed services, the lieutenant is known to be a starting rank for a commissioned officer. A lieutenant is a gazetted officer under the Indian government.
3. Captain
The captain is the biggest rank a soldier may attain when they are still serving on the field. The rank has been there since the 1560s and exists in various countries. Right after a couple of years of notable commissioned service, a soldier may become a captain.
4. Major
The rank of a major is two levels greater than that of a lieutenant and a single rank higher than that of a Captain. It is exciting to know that a major is in charge of diverse tactical duties and responsibilities, along with directing and commanding the military force.
5. Lieutenant Colonel
The regiments and battalions in the armed forces are under the control of a lieutenant colonel. Contrary to an NCO in Indian army, an officer may become a lieutenant Colonel after finishing 13 years of commissioned duty.
6. Colonel
The rank of a Colonel in the Indian Army is identical to that of a captain in the Indian Navy and a group captain in the Indian Air Force. A Colonel’s rank is just one level higher than a lieutenant colonel.
7. Brigadier
These officers hold a one-start rank in the Indian Army. The position of Brigadier is comparable to that of an air Commodore of the Indian Air Force.
8. Major General
The major general position is equal to the earlier rank of sergeant major general. The rank is just higher than a Brigadier and lower than a lieutenant general.
9. Lieutenant General
An officer who is a lieutenant general has a three-star military rank in the Indian Army. After the completion of 36 Years of commissioned service, the military officers may undergo a selection process to become lieutenant general.
10. General
If you are thinking which rank is a four-star, then the general officer is the answer. It is the highest rank in many of the armies now in operation.
B. Indian Navy Ranks
1. Sub-Lieutenant
An officer of entry-level rank in the Indian Navy. These officers are equal to the second lieutenant in the army.
2. Lieutenant
It is more of a junior officer rank who has the responsibility for managing sections and small units.
3. Lieutenant Commander
Yes, you predicted it right! Lieutenant Commander is a rank higher than the lieutenant. They are responsible for managing divisions and departments aboard ships.
4. Commander
These are senior officers in Command of a small shore establishment or combatant vessel.
5. Captain
These are the officers in Command for larger vessels.
6. Commodore
These officers have bigger management takes as they are responsible for commanding a group of ships.
7. Rear Admiral
These are the senior flag officers who are responsible for commanding a group of ships.
8. Vice Admiral
If you are under the impression that they have different duties than rear Admiral, then you are right.
9. Admiral
In the Navy, the highest-ranking officer is the Admiral. They are responsible for tactical decision-making and overall Command.
You May Also Like: How to Write a Follow-Up Email After an Interview
C. Indian Air Force Ranks
1. Flying Officer
This position is equivalent to the second lieutenant in the army or navy’s sub-lieutenant.
2. Flight Lieutenant
It is the rank of a junior officer who is responsible for leading small groups.
3. Squadron Leader
These are the mid-ranking officers. However, you would be thrilled to know that they have authority over a Squadron of aircraft.
4. Wing Commander
They are responsible for Wing commanding.
5. Group Captain
They are responsible for commanding a large airbase.
6. Air Commodore
Commanding a major operational base is the sole responsibility of these professionals.
7. Air Vice Marshal
Their duty is to command a major operational or functional division within the Air Force.
8. Air Marshal
These officers make sure to command a major area of an air force.
9. Air Chief Marshal
Yes, you guessed it right, it is the highest rank in the air force.
You May Also Find Interesting:
| HR Officer Job Description | Chief Operating Officer Job Description |
| Purchasing Officer Job Description | Finance Officer Job Description |
Duties and Responsibilities of Commissioned Officers in the Indian Military
Another interesting fact that we will discuss now is that the responsibilities of a commissioned officer vary a lot from those of a non-commissioned army officer. Here are some of the roles of commissioned officers:
A. Leadership and Command
- Guiding and Leading military personnel in different missions and operations.
- Making vital decisions and ensuring the triumph and safety of the unit.
B. Planning and Execution
- Coordinating with various other branches and units to achieve the aims and objectives of the mission.
- Coming up with tactical plans perfectly executing them.
C. Administration and Management
- Make sure of adherence to compliance and policies in order to maintain operational efficiency.
- Managing the resources.
D. Training and Development
- Coaching and mentoring the subordinates to foster professional excellence and growth.
- Overseeing and conducting training programs to enhance readiness and skills.
Becoming a Commissioned Officer in the Indian Military
Here is what you need to know to become a Commissioned Officer in the Indian Army:
A. Educational Requirements
- The aspiring officers need to have a bachelor’s degree from a reputed university.
- Various entry schemes may have certain educational needs tailored to the programs.
B. Entry Schemes
- National Defence Academy (NDA): Aspirants may join the NDA after finishing their 12th.
- Indian Military Academy (IMA): The graduates may join the IMA via direct entry or go through training to become Commissioned officers.
- Officers Training Academy (OTA): Both women and men may join OTA after graduation.
- University Entry Scheme (UES): It allows the final year engineers to join the army.
- Technical Graduate Course (TGC): Engineers may join the army with this course.
C. Selection Process
- The candidates go through a written test, which changes depending on the entry schemes.
- The qualifiers go through the SSB interview
- Finally, the candidates go through the medical examinations to see if they meet the requirements.
D. Training and Commissioning
- The selected candidates undergo various rigorous training at different academies.
- After the completion of training, the aspirants are commissioned as officers.
You May Also Like: Top Aviation Courses after 12th
Career Progression and Advancement in the Indian Military
Let us take a look at the advancement and career progression in the Indian Military:
A. Promotions and Tenure
- In the military, promotion is dependent on requirements of time-in-grade and evaluations of performances.
- The promotion board reviews the performance of the candidates and selects the ones for Promotion, depending on their merit and performance.
B. Professional Military Education (PME)
- The officers go through different professional military education programs to increase their tactical and leadership traits.
- There are programs such as DSSC, NDC, and HCC that prepare officers for staff positions.
C. Specialization and Staff Assignments
- Officers may go for specialization courses in their own branches to develop expertise in certain areas.
- They can also serve in instructional appointments where they may contribute to the training.
- The officers also may be deputed to other enterprises and ministries.
Challenges and Considerations for Commissioned Officers in the Indian Military
So what are the challenges? We have put together some of the common considerations and challenges for the officers as well.
A. Balancing leadership and management responsibilities
Commissioned officers need to effectively balance their troops and operations as well as manage logical and administrative tasks to ensure smooth functioning.
B. Adapting to evolving security threats and technological advancements
It is a must for the officers to stay updated on the up-and-coming threats in security and technological advancements to counter the new challenges and maintain tactical advancements effectively.
C. Maintaining physical and mental fitness
Military service officers need to maintain peak physical fitness to carry out their duties effectively, and they also need to take care of their mental well-being.
D. Balancing military service with personal and family life
They also often face challenges balancing the requirements of military service demands and family commitments.
More Articles:
| Safety Officer Job Description | Marketing Officer Job Description |
| HR Admin officer Job Description | Public Relations Officer Job Description |
Conclusion
So there you have it! We have addressed all the types of a commissioned officer as well as their duties and the challenges that they have faced. Now that you have read this far, you are also aware of the different ranks in the Indian Army and Navy.
FAQs on Commissioned Officer Types, Ranks and Duties
Q1. What is a permanent commission?
A1. A permanent commission is basically a commitment to the military until retirement.
Q2. What is the CDS exam?
A2. The UPSC carries out the CDS test twice a year among university graduates or those who are in their last years of study.
Q3. What are the commissioned officers in charge of?
A3. The commissioned officers are in charge of training and commanding the troops that are enlisted.
Q4. Who can join the armed forces?
A4. All the citizens of India, irrespective of their class, caste, community, and religion, can join the armed forces and become commissioned officers.
People Are Also Intereted In:
- Top 20 Professional Skills [Tips and Examples]
- 10 Essential Decision-Making Skills With Examples
- Basic Maths Skills: Types, Examples and Strategies
- Active Listening Skills: Definition, Techniques, & Examples